Fem pop bypass cpt code – Femoral popliteal bypass CPT code, the cornerstone of this informative article, invites you to delve into a world of surgical precision and medical expertise. We will explore the intricate details of this procedure, its indications, and the intricacies of billing and documentation.
As we embark on this journey, we will uncover the nuances of preoperative considerations, postoperative care, and potential complications. Along the way, we will shed light on alternative treatment options, empowering you with a comprehensive understanding of this critical surgical intervention.
Femoral Popliteal Bypass Surgical Procedure: Fem Pop Bypass Cpt Code
A femoral popliteal bypass surgery is a procedure that creates a new pathway for blood to flow around a blocked or narrowed artery in the leg. This surgery is typically performed to treat peripheral artery disease (PAD), a condition in which the arteries in the legs become narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow to the lower extremities.
The goal of a femoral popliteal bypass surgery is to restore blood flow to the leg and relieve symptoms of PAD, such as pain, numbness, and cramping. The surgery involves taking a healthy blood vessel from another part of the body, such as the saphenous vein in the leg, and grafting it to the blocked or narrowed artery.
Surgical Procedure
A femoral popliteal bypass surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia. The surgical procedure involves the following steps:
- Incision:The surgeon makes an incision in the groin area and another incision in the back of the knee.
- Surgical Approach:The surgeon locates the blocked or narrowed artery and the healthy blood vessel that will be used for the bypass graft.
- Grafting:The surgeon removes the healthy blood vessel from its original location and attaches it to the blocked or narrowed artery, creating a new pathway for blood to flow.
- Closure:The surgeon closes the incisions with stitches or staples.
After the surgery, the patient will be monitored closely for any complications. The recovery time for a femoral popliteal bypass surgery typically takes several weeks, and the patient may need to use crutches or a walker during this time.
CPT Code 35525: Femoral Popliteal Bypass
CPT code 35525 represents a surgical procedure involving the creation of a bypass graft between the femoral artery and the popliteal artery. This bypass is performed to restore blood flow to the lower leg when the original arteries have become blocked or narrowed.The
components of CPT code 35525 include:
Surgical approach
Open surgical approach, which involves making an incision in the groin and another incision in the popliteal fossa.
Surgical technique
End-to-end anastomosis, where the graft is connected to the femoral artery and the popliteal artery.To ensure accurate billing for CPT code 35525, the following documentation requirements must be met:
Preoperative diagnosis
Documentation of the underlying condition, such as peripheral artery disease or atherosclerosis, that necessitated the bypass procedure.
Operative report
A detailed description of the surgical procedure, including the surgical approach, the type of graft used, and any intraoperative complications.
Postoperative care plan
A summary of the patient’s postoperative care, including any medications, wound care instructions, and follow-up appointments.
Indications for Femoral Popliteal Bypass
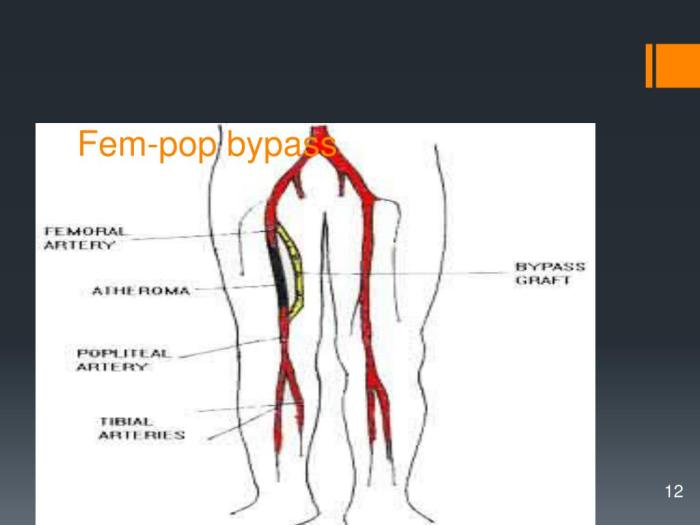
A femoral popliteal bypass is a surgical procedure performed to restore blood flow to the lower leg when the main artery in the thigh (femoral artery) and the artery behind the knee (popliteal artery) become blocked or narrowed. This blockage can lead to severe pain, numbness, and even tissue damage in the leg and foot.
Medical Conditions Necessitating Femoral Popliteal Bypass
- Atherosclerosis:A buildup of plaque in the arteries, which can narrow the femoral and popliteal arteries.
- Thrombosis:The formation of a blood clot in the femoral or popliteal artery.
- Popliteal Artery Entrapment Syndrome (PAES):A condition where the popliteal artery is compressed by surrounding muscles or tendons.
- Trauma:Injuries that damage the femoral or popliteal artery.
Diagnostic Tests and Criteria
To determine the need for a femoral popliteal bypass, doctors use various diagnostic tests, including:
- Physical examination:Checking for symptoms such as pain, numbness, and weakness in the leg.
- Doppler ultrasound:A non-invasive test that uses sound waves to measure blood flow in the arteries.
- Angiogram:An X-ray procedure that uses a contrast dye to visualize the arteries and identify blockages.
The decision to perform a femoral popliteal bypass is based on the severity of the blockage, the symptoms experienced by the patient, and the results of the diagnostic tests.
Patient Selection Criteria
Patients who are considered candidates for a femoral popliteal bypass typically meet the following criteria:
- Severe symptoms that significantly impact their quality of life.
- A high risk of developing serious complications, such as tissue damage or amputation.
- No other viable treatment options available.
Preoperative Considerations
Before undergoing a femoral popliteal bypass, patients undergo thorough preoperative assessment and preparation to optimize surgical outcomes and minimize risks.
Preoperative preparation includes a comprehensive medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests to assess the patient’s overall health, cardiovascular status, and suitability for the procedure.
Preoperative Assessment
- Medical history:Review of past medical conditions, current medications, allergies, smoking history, and lifestyle factors.
- Physical examination:Assessment of vital signs, cardiovascular system (including heart rate, blood pressure, and peripheral pulses), and the affected limb.
- Diagnostic tests:Blood tests, electrocardiogram (ECG), chest X-ray, and imaging studies (such as ultrasound or angiography) to evaluate the extent of arterial disease, identify suitable bypass sites, and assess overall cardiovascular health.
Preoperative Instructions
- Fasting:Patients are instructed to fast for a specific period before surgery, typically 8-12 hours.
- Medications:Patients are advised to continue taking essential medications unless otherwise instructed by the surgeon.
- Smoking cessation:Smoking is strongly discouraged before and after surgery as it impairs wound healing and increases the risk of complications.
- Skin preparation:Patients are instructed to clean the surgical site thoroughly and avoid shaving the area.
Informed Consent and Patient Education
Informed consent is obtained from the patient after thorough discussion of the procedure, its benefits, risks, and potential complications. Patient education is crucial to ensure they understand the procedure and actively participate in their care.
Postoperative Care and Management
After a femoral popliteal bypass, patients require meticulous monitoring and postoperative care to ensure optimal outcomes. The immediate postoperative period involves continuous surveillance of vital signs, wound assessment, and pain management.
Fem pop bypass cpt code is a surgical procedure that involves creating a new opening between the aorta and the pulmonary artery. This procedure is often performed to treat patients with congenital heart defects. In the painting “El Manto de la Verónica” ( el manto de la veronica ), the artist depicts the moment when Veronica wipes the face of Jesus with a cloth, leaving an imprint of his face on the cloth.
The cloth is said to have miraculous powers, and it is believed to have been used to heal the sick. The fem pop bypass cpt code is a similar procedure, as it also involves creating a new opening between two blood vessels.
This procedure can be used to treat a variety of heart conditions, and it is often performed on patients who have congenital heart defects.
Wound Care
Wound care is crucial to prevent infection and promote healing. The surgical incision is typically dressed with sterile gauze and secured with a bandage. Wound care protocols involve regular dressing changes, monitoring for signs of infection, and keeping the wound clean and dry.
Pain Management
Pain management is essential for patient comfort and recovery. Medications such as opioids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and local anesthetics are commonly used to alleviate pain. Pain levels are monitored regularly, and medications are adjusted accordingly.
Mobilization
Early mobilization is encouraged to prevent blood clots and promote healing. Patients are usually assisted to walk within 24 hours after surgery. Progressive ambulation is gradually increased as tolerated, with close monitoring for any complications.
Discharge Criteria and Follow-up Plan
Patients are typically discharged from the hospital within 3-5 days after surgery, depending on their recovery progress. Discharge criteria include stable vital signs, adequate pain control, absence of wound complications, and ability to ambulate safely.Follow-up appointments are scheduled regularly to monitor wound healing, check for signs of infection, and assess overall recovery.
Patients are advised to follow specific instructions regarding activity restrictions, wound care, and medication adherence.
Potential Complications
Femoral popliteal bypass surgery is generally safe and effective, but as with any surgery, there are potential complications that can occur. These complications can be divided into early complications (occurring within the first 30 days after surgery) and late complications (occurring more than 30 days after surgery).
The most common early complications include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Graft failure
The most common late complications include:
- Stenosis (narrowing) of the graft
- Aneurysm (bulging) of the graft
- Graft occlusion (blockage)
Risk Factors and Preventive Measures, Fem pop bypass cpt code
The risk of complications from femoral popliteal bypass surgery is influenced by a number of factors, including the patient’s age, overall health, and the severity of their underlying condition. Other risk factors include:
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- History of previous surgery or radiation therapy in the area of the surgery
There are a number of things that can be done to reduce the risk of complications from femoral popliteal bypass surgery, including:
- Quitting smoking
- Managing diabetes and high blood pressure
- Losing weight if obese
- Following the doctor’s instructions carefully before and after surgery
Management and Treatment of Complications
If complications do occur, they can be treated with a variety of methods, depending on the severity of the complication. Treatment options may include:
- Medications
- Surgery
- Angioplasty (a procedure to open up a blocked artery)
- Stenting (a procedure to place a stent in a narrowed artery)
Alternative Treatment Options
For patients who are not suitable candidates for a femoral popliteal bypass, alternative treatment options are available. These include:
- Endovascular therapy: This minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a catheter into the blocked artery and using a balloon to widen it. It is less invasive than surgery and has a shorter recovery time, but it may not be suitable for all patients.
- Stenting: This procedure involves inserting a stent, a small mesh tube, into the blocked artery to keep it open. It is similar to endovascular therapy but may be more effective in some cases.
- Medication: Medications such as aspirin, clopidogrel, and statins can help to prevent blood clots and improve blood flow. They are often used in combination with other treatments.
- Lifestyle changes: Making healthy lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a healthy diet, can help to improve circulation and reduce the risk of further blockages.
The decision about which treatment option is most appropriate for a particular patient depends on a number of factors, including the severity of the blockage, the patient’s overall health, and their preferences. The doctor will discuss the options with the patient and help them make the best decision.
FAQ Insights
What is the purpose of a femoral popliteal bypass?
Femoral popliteal bypass aims to restore blood flow to the lower leg by creating a new pathway around a blocked or narrowed artery.
What are the indications for a femoral popliteal bypass?
Femoral popliteal bypass is indicated in patients with severe peripheral artery disease, such as critical limb ischemia or claudication.
How is a femoral popliteal bypass performed?
The procedure involves harvesting a vein from another part of the body and grafting it to the femoral artery and popliteal artery, bypassing the blocked or narrowed segment.