Embark on a scientific odyssey with our elements and macromolecules in organisms worksheet answer key, a comprehensive guide that unlocks the intricate world of life’s building blocks. Delve into the fundamental elements that orchestrate biological processes and explore the remarkable macromolecules that shape the very fabric of living systems.
This meticulously crafted resource unravels the secrets of element interactions, revealing their profound impact on macromolecule structure and function. Witness how these fundamental components intertwine to orchestrate the symphony of life.
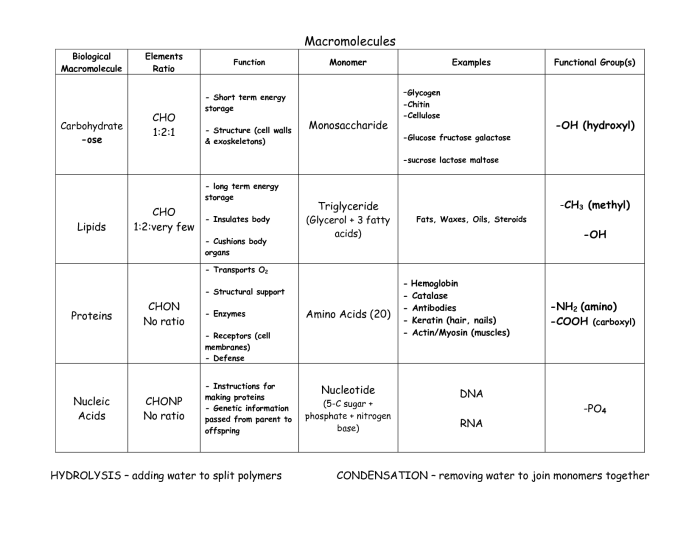
Elements in Organisms: Elements And Macromolecules In Organisms Worksheet Answer Key
Living organisms are composed of a variety of chemical elements. These elements are essential for life and play crucial roles in biological processes.
The most abundant elements in living organisms are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus. These elements make up the majority of organic molecules, which are the building blocks of life.
Other essential elements include sulfur, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sodium, and chlorine. These elements are involved in a wide range of biological processes, such as energy production, muscle contraction, and nerve transmission.
Functions and Roles of Elements in Biological Processes, Elements and macromolecules in organisms worksheet answer key
- Carbon: Forms the backbone of organic molecules, including carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids.
- Hydrogen: Involved in chemical reactions and helps to form bonds between atoms.
- Oxygen: Essential for respiration and is used to generate energy.
- Nitrogen: Component of proteins and nucleic acids, which are essential for cell growth and function.
- Phosphorus: Involved in energy storage and transfer, and is a component of cell membranes.
- Sulfur: Found in amino acids and proteins, and is involved in enzyme function.
- Potassium: Essential for maintaining cell membrane potential and nerve function.
- Calcium: Involved in bone formation, muscle contraction, and blood clotting.
- Magnesium: Component of chlorophyll and is involved in photosynthesis.
- Sodium: Involved in maintaining fluid balance and nerve function.
- Chlorine: Component of hydrochloric acid in the stomach and is involved in digestion.
Interactions Between Elements to Form Molecules and Compounds
Elements interact with each other to form molecules and compounds. These interactions are governed by chemical bonds, which are the forces that hold atoms together.
The type of chemical bond formed depends on the properties of the elements involved. For example, carbon atoms can form covalent bonds with other carbon atoms or with other elements, such as hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen.
The formation of molecules and compounds is essential for life. These molecules and compounds provide the building blocks for cells and tissues, and they are involved in a wide range of biological processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the essential elements found in living organisms?
The essential elements for life include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sodium.
How do elements interact with macromolecules to form complex biological structures?
Elements interact with macromolecules through covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and hydrogen bonds. These interactions determine the structure and function of macromolecules.
What are the practical applications of understanding elements and macromolecules?
Understanding elements and macromolecules has applications in biotechnology, drug development, food science, and agriculture.